 mmap
mmap
mmap是操作系统提供的一个内存映射文件的方法,即将一个文件或者其它对象映射到进程的地址空间,实现文件磁盘地址和进程虚拟地址空间中一段虚拟地址的一一对映关系。实现这样的映射关系后,进程就可以采用指针的方式读写操作这一段内存,而系统会自动回写脏页面到对应的文件磁盘上,即完成了对文件的操作而不必再调用read,write等系统调用函数。相反,内核空间对这段区域的修改也直接反映用户空间,从而可以实现不同进程间的文件共享。
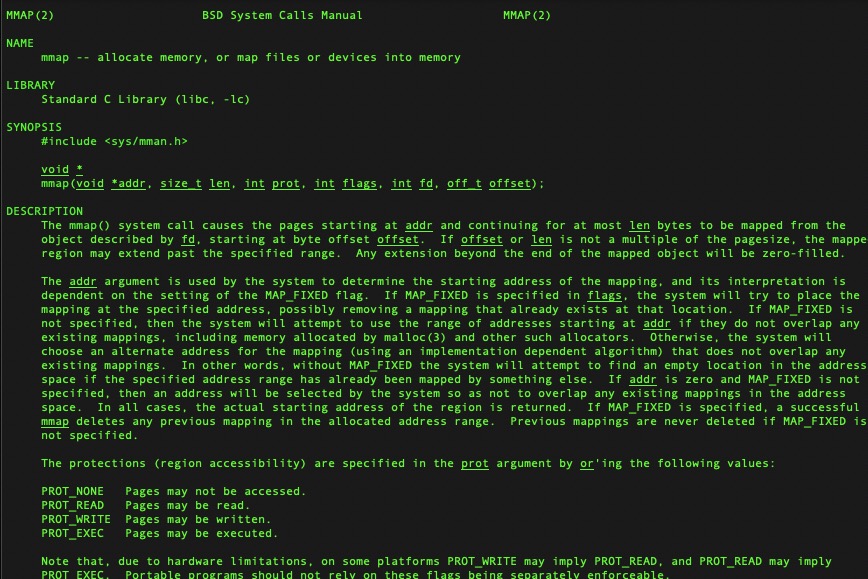
我们通过man mmap命令可以看到如下信息:
# include <fcntl.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# include <stdio.h>
# include <sys/types.h>
# include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>
void doMmap()
{
int fd = open("tmp/mmap.txt", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open_error");
exit(1);
}
ftruncate(fd, 0);
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
char *data = "hello world";
int len = strlen(data);
write(fd, data, strlen(data));
// 文件大小为0,不能创建映射区,offset必须为页大小整数倍4096
char *mem = mmap(NULL, 20, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (mem == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap error");
exit(1);
}
printf("映射区文件内容:%s\n", mem);
if (munmap(mem, len) == -1) {
perror("munmap error");
exit(1);
}
close(fd);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
上次更新: 2022/12/01, 11:09:34
